Research Topic
Our research group elaborates effects of ionizing and non-ionizing radiations on genome stability in human cells with focus on hematological stem cells. An effect of radiations on origination of leukemia, molecular mechanisms in etiology of leukemia and new approaches in prevention, treatments, diagnostics and relapse prevention of leukemia are being investigated.
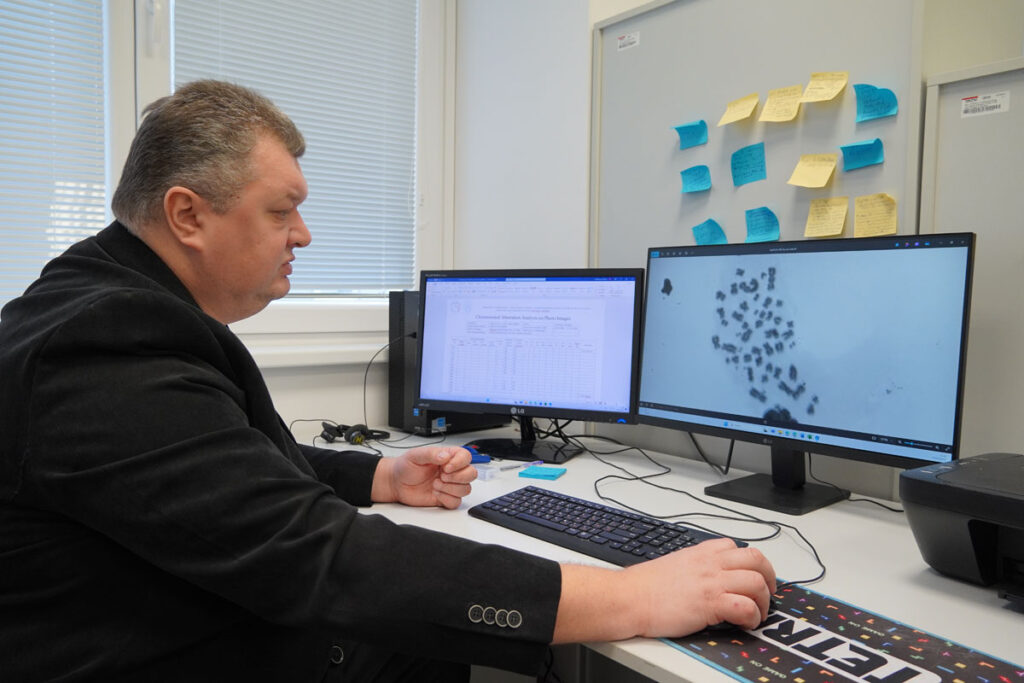
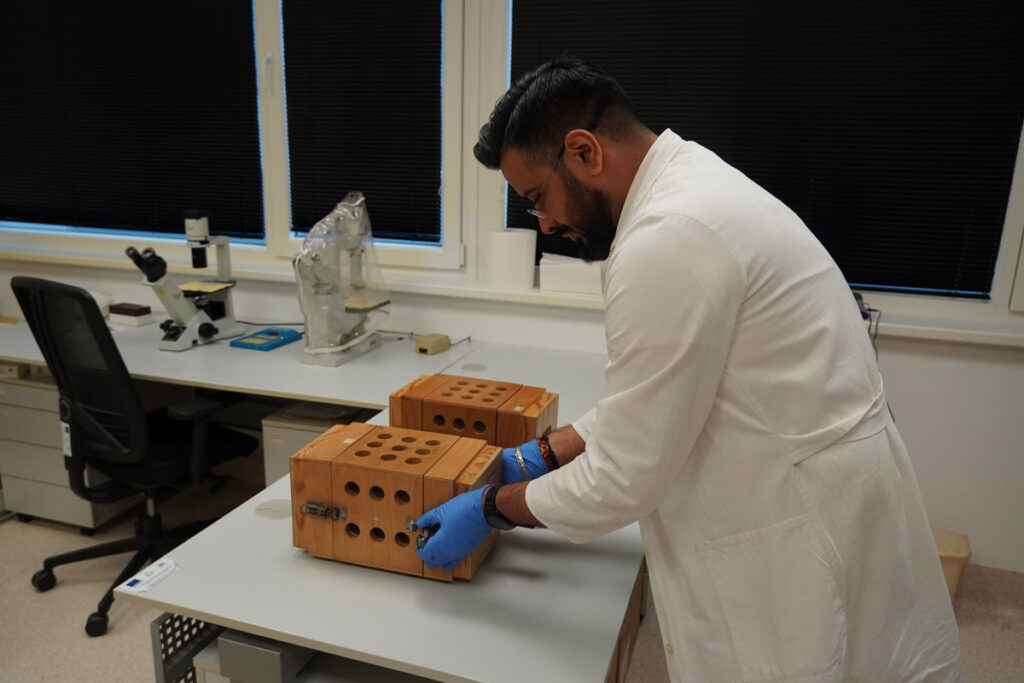
DNA damage response, circular RNA, microRNA and long noncoding RNA, gene and chromosome rearrangements, gene expression, and apoptosis are the main endpoints studied by the state-of-the-art techniques including automated fluorescent and imaging microscopy, DNA repair foci and comet assays, chromosomal aberrations, micronuclei, FISH, RT-qPCR, DNA cloning and sequencing, standard and imaging flow cytometry, and cell sorting linked with hematopoietic stem cells explansion.
New emerging possibilities of using non-ionizing radiation in medicine, on one side, and increasing health risks from exposures to low doses of ionizing radiation and low intensity non-ionizing radiation, from another side, are in focus of research projects.
We contributed to development of new approaches for inhibition of cancer cell growth with extremely low frequency magnetic fields, mapping of magnetic fields from mobile communication devices in human body, and radiobiological studies for implementation of therapeutic proton complex at Ružomberok.
Special efforts are given to establishing biomarkers for assessment of individual radiosensitivity of cancer patients, reduction of side effects of radiotherapy and health risks from exposure to radiofrequency radiation of mobile communication.
The RT has also contributed to biological dosimetry, i.e. in medical radiologists and patients. In the radiological workers we found an accumulation of radiation-induced chromosomal damage and an amplification of the MLL gene segment that could potentially contribute to malignant transformation.
We also compared genetic instability in people leaving in proximity to 3G/4G mobile phone base stations (BS). Statistically significant correlation of chromosomal aberrations with distance to BS/intensity of radiofrequency radiation (RFR) was established and the equal dose of ionizing radiation was estimated based on dicentrics according to the IAEA recommendations.
The work in progress is to: (i) evaluate possible genetic damage induced by MRI investigations, (ii) shield RFR in order to reduce symptoms of burn-out syndrome, and (iii) evaluate clinical effects of phytochemicals in cancer patients during radiotherapy.
Photo Gallery





Head of the Research Group

Igor Belyaev, PhD, DrSc. (118 CC publications, 2547 ISI citations, h-index 29) is an expert in radiation physics, radiobiology, and genetic toxicology. He has worked in Russia, Sweden, the USA, Germany, Austria, and Slovakia, leading over 20 research projects. He is a member of WHO EMF Project, IARC, DG SANCO EC, EUROPAEM, ECERI, and the Bioelectromagnetics Society. He serves as Associate Editor of an international journal in radiation biology and was awarded for the most significant bioelectromagnetics publication (2006–2010).



